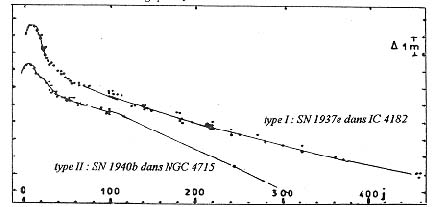
Supernovae (B Cas, CM Tau). Stars that increase, as a result of an outburst, their brightnesses by 20 mag and more, then fade slowly. The spectrum during an outburst is characterized by the presence of very broad emission bands, their widths being several times greater than those of the bright bands observed in the spectra of novae. The expansion velocities of SN envelopes are in the thousands of km/s. The structure of a star after outburst alters completely. An expanding emission nebula results and a (not always observable) pulsar remains at the position of the original star. According to the light curve shape and the spectral features, supernovae are subdivided into types I and II.

Return to the page "cataclysmic variables"
Return to the page "typology"
Return to the AFOEV home page